
BEIJING, Dec. 16, 2025 -- METiS TechBio ("METiS") today announced that two of its oncology pipeline candidates, MTS-105 and MTS-107, have been published in leading international peer-reviewed journals, Nature Communications and the Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer (JITC), representing two major breakthroughs in mRNA-based cancer therapeutics.
Both studies leverage METiS's proprietary AI-powered NanoForge platform, which introduces a precision-guided rocket-and-payload delivery analogy. By combining liver- and spleen-targeted lipid nanoparticle (LNP) delivery systems with programmable mRNA engineering, METiS has developed a new generation of immunotherapy strategies capable of efficiently activating antitumor immunity in specific organs in vivo.
MTS-105 is a first-in-class mRNA-encoded T cell engager (TCE) therapy candidate for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), delivered via METiS's proprietary liver-targeted LNP system. Study results demonstrate that, once delivered to and taken up within the liver, the mRNA is translated in situ and secreted locally as high level of bispecific antibodies, which rapidly penetrate HCC tissues. Employing this "Trojan Horse" strategy, MTS-105 efficiently activates T cells within the tumor to induce tumor cell killing, achieving complete tumor clearance and long-term T cell immune memory in mouse models.
MTS-105 provides a breakthrough solution to the long-standing limitations of protein-based TCEs in solid tumors, positioned as the world's first mRNA-encoded TCE therapy for solid tumors. The program has now entered clinical development.
MTS-107 is an innovative mRNA therapeutic vaccine targeting HPV16/18-positive cervical and head and neck cancers, with potential to achieve breakthrough treatment for HPV-associated cancers. Using spleen-targeted LNPs, METiS's team designed a construct combining dual E6/E7 antigens with a novel immune-activating adjuvant. In mouse models, MTS-107 demonstrated synergistic antitumor activity with PD-1 checkpoint inhibitors, resulting in robust expansion of HPV-specific CD8⁺T cells. MTS-107 will continue into original clinical exploration.
Chris LAI, Co-founder and CEO, said:
"This is an important milestone demonstrating the power of METiS's AI-driven NanoForge platform in therapeutic development. In conventional cancer therapy, most 'soldiers' remain outside the tumor, unable to infiltrate solid tumors for precise, effective killing. Our 'rocket-and-satellite' precision delivery paradigm has been strongly validated in these studies. We look forward to advancing global clinical development with our partners, bringing targeted therapies to patients and offering hope for survival or even cure."
Dr. Wei XU, Chief Scientific Officer and corresponding author of two studies, added:
"mRNA therapeutics have long been constrained by delivery challenges, and innovation in LNP technology is essential for unlocking their full potential. MTS-105 is the first to show that an Fc-free bispecific T cell engager can activate T cells without driving exhaustion, while MTS-107 introduces a new antigen design and built-in adjuvant that markedly enhance antitumor immunity.
A recent Nature study reported that patients treated with PD-1 inhibitors nearly doubled their three-year survival if they had also received an mRNA COVID-19 vaccine—a finding that strongly aligns with our observations for MTS-107. These results highlight how mRNA platforms can synergize with PD-1 blockade and signal a new chapter for immuno-oncology"
Dr. Andong LIU, Vice President and Head of Platform Technologies, and co-corresponding author of the Nature Communications study, stated:
"Our NanoForge engine significantly accelerates LNP and mRNA design cycles, boosting delivery efficiency and safety for liver- and spleen-targeted therapeutics. LNP nanodelivery is critical for precise tissue targeting and effective antitumor therapy. These studies open broad new avenues for innovative mRNA therapeutics."
MTS-105: Preclinical Breakthrough in Nature Communications
On December 15, Nature Communications (IF 15.7, 2024) published METiS's preclinical study titled:
"Organ-Specific Delivery of an mRNA-Encoded Bispecific T Cell Engager Targeting Glypican-3 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma."

Key highlights:
- Organ-Specific Delivery: MTS-105 achieves highly efficient liver-targeted delivery with minimal systemic exposure. Studies in mice, rats, and cynomolgus monkeys show superior hepatic enrichment compared to antibody-based TCEs.
- Controlled Release and Safety: Reduced C max and systemic exposure lower toxicity risks. In cynomolgus monkeys, linear pharmacokinetics were observed with excellent tolerability, supporting potential weekly dosing.
- Potent Antitumor Efficacy: Data from mouse models showed a marked increase in intratumoral exposure, enabling 100% complete responses—with full tumor clearance—at doses as low as 0.15 μg. In contrast, the protein-based TCE control achieved only ~50% tumor growth inhibition even at 1 mg/kg (approximately 20 μg).
- Durable T Cell Memory: Cured mice remained tumor-free upon rechallenge, indicating long-term immune memory and prevention of recurrence.
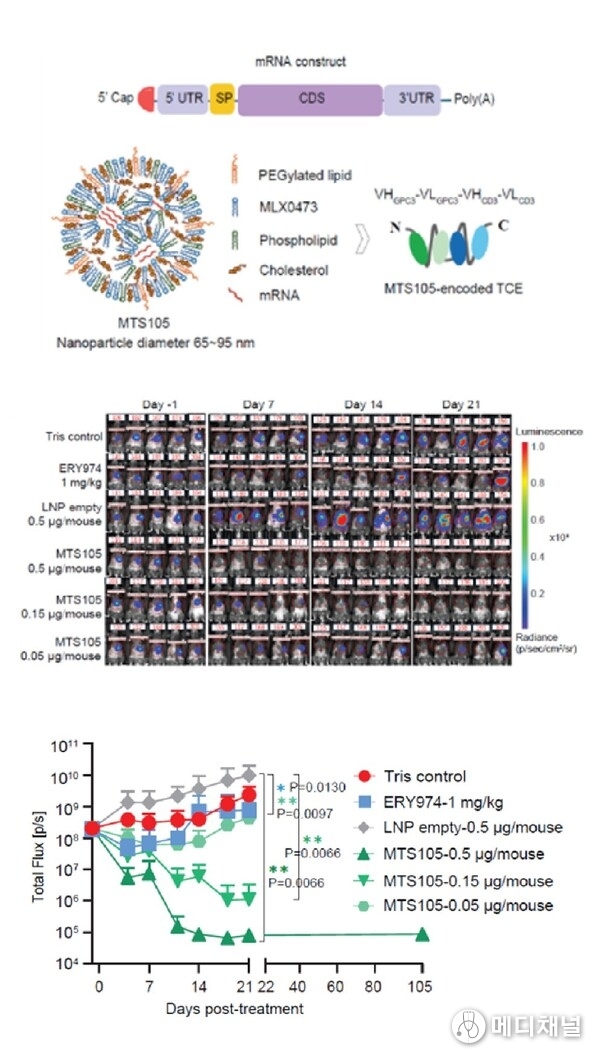
MTS-105 sets a new paradigm for translating TCE therapy into solid tumors, paving the way for first-in-class mRNA-encoded TCE therapy.
MTS-107: Breakthrough HPV Vaccine Published in JITC
On September 17, JITC published: "mRNA-encoded mutant HPV16/18 vaccines promote specific T-cell responses and synergize with anti-PD-1 checkpoint blockade in mediating therapeutic tumor regression in mice."

Key findings:
- Complete Tumor Regression: In advanced HPV18⁺MC38 tumor models, MTS-107 combined with PD-1 blockade achieved 100% complete response (CR).
- Spleen-Targeted LNP Delivery: Enhances antigen presentation and T cell activation.
- Dual-Subtype Antigen Design: Encodes mutated HPV16/18 E6/E7 antigens; optimized mRNA sequences improve translation and stability.
- Built-in Adjuvant: Co-expresses GM-CSF to promote dendritic cell maturation and HPV-specific CD8⁺T cell activation.
- Synergy with PD-1 Blockade: While monotherapy expands tumor-infiltrating HPV-specific T cells; combination with PD-1 blockade relieves immune suppression for complete tumor regression.
This work demonstrates the transformative potential of AI-powered mRNA vaccines in HPV-associated cancers and establishes METiS's innovation at the intersection of AI-driven nanodelivery and tumor immunotherapy, providing a strong foundation for clinical translation.
*Reference: Grippin, et al. Nature 2025, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-025-09655-y
